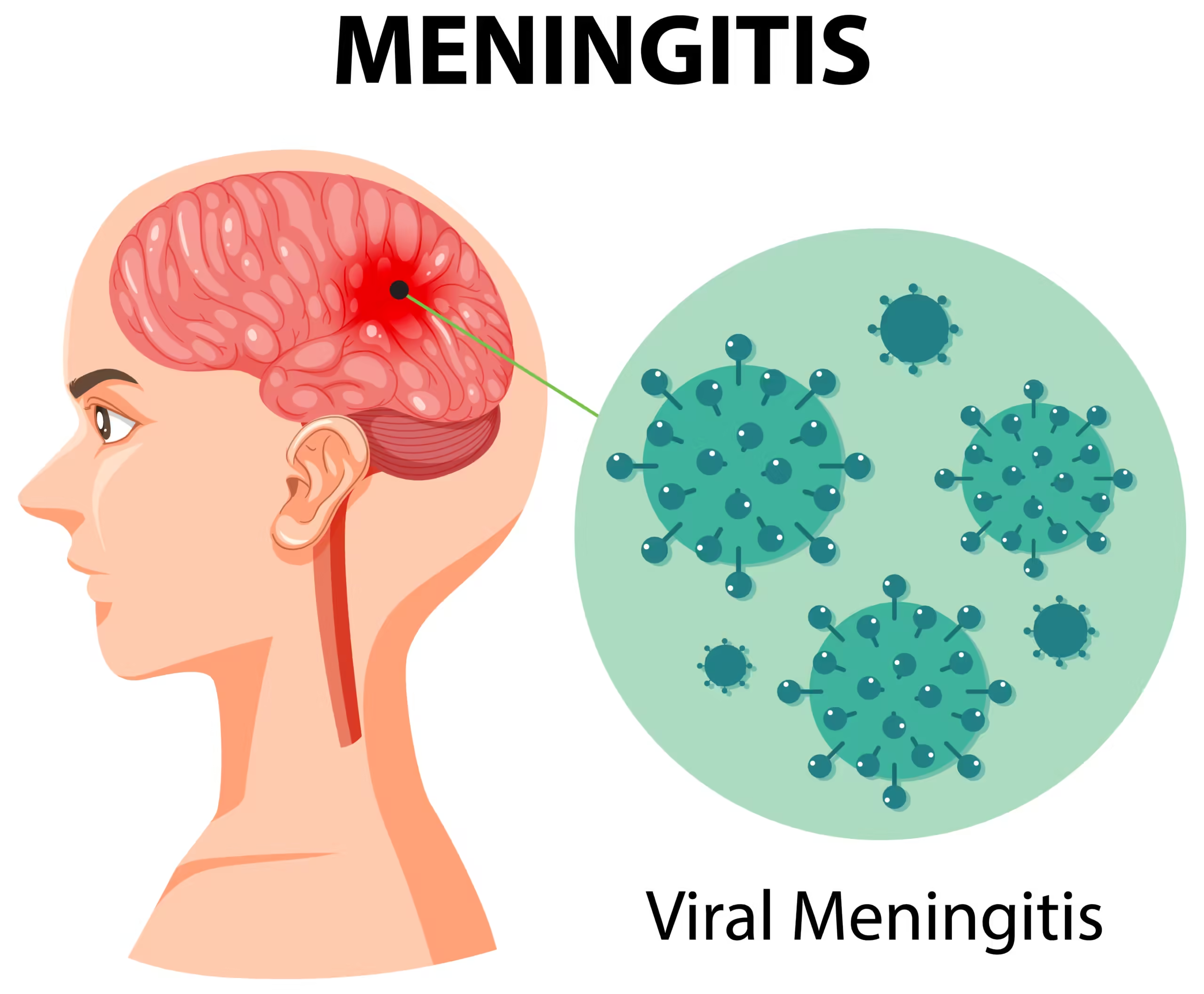
what is meningitis definition
Meningitis is a severe clinical condition characterized by way of inflammation of the meninges, the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord. It may be due to bacterial, viral, or fungal infections, with bacterial meningitis being the most excessive form. Symptoms usually consist of unexpected fever, severe headache, stiff neck, sensitivity to light, nausea, and altered intellectual status.
Bacterial meningitis can lead to fast fitness deterioration and is taken into consideration a clinical emergency requiring immediate antibiotic remedy. Viral meningitis is normally less excessive and often resolves with out particular treatment. Diagnosis includes reading cerebrospinal fluid obtained through a lumbar puncture.
Vaccination can save you positive forms of bacterial meningitis, extensively the ones due to Neisseria meningitidis and Streptococcus pneumoniae. Prompt scientific attention is vital, as untreated meningitis can result in severe headaches inclusive of brain damage, listening to loss, or maybe demise. Early intervention and preventive measures significantly enhance outcomes.
Do I Have Meningitis Quiz?
Meningitis is a dangerous illness that needs to be treated right away. It is an inflammation of the meninges, which are the membranes that coat the brain and spinal cord. Infections with bacteria, viruses, or other microbes can cause this illness; less frequently, certain medications might cause it. You can determine whether you need to see a doctor right away if you’re having symptoms that you think could be related to meningitis by taking this quiz.
Understanding the Symptoms
The symptoms of meningitis might appear over a few days or over several hours. If a person is older than two, common symptoms and indicators include:
Unexpectedly high temperature: One of the most typical signs of meningitis is a high fever.
Stiff neck: It may be challenging to touch the chin to the chest when there is stiffness in the neck.
Headache that is severe: This type of headache is typically characterized as being excruciating and distinct from a regular headache.
Vomiting and nausea: These symptoms frequently coincide with headaches.
Photophobia, or sensitivity to light: Strong lights can be uncomfortable.
Disorientation or trouble focusing: Shifts in mental state are frequent.
Excessive tiredness or difficulty waking up: These symptoms may indicate a serious medical condition.
Skin rash (occasionally): Meningococcal meningitis can result in a rash.
Take the Quiz
Are you experiencing a sudden high fever?
Yes
No
Do you have a severe headache that seems different from usual?
Yes
No
Is your neck stiff and does it hurt to touch your chin to your chest?
Yes
No
Are you feeling nauseous or have you vomited recently?
Yes
No
Are you unusually sensitive to bright lights?
Yes
No
Are you feeling confused or having trouble concentrating?
Yes
No
Are you excessively sleepy or finding it hard to wake up?
Yes
No
Do you have a rash that doesn’t fade under pressure (glass test)?
Yes
No
Interpreting Your Results
If you answered “Yes” to two or more of these questions, it’s important to seek medical attention immediately. While this quiz isn’t a definitive diagnostic tool, the symptoms of meningitis are serious and require professional evaluation. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for the best outcomes.
Meningitis B Vaccine Information Statement (VIS)
The Neisseria meningitidis serogroup B bacteria that causes meningitis B can be fatal, and young people—including teenagers and college studentsare particularly vulnerable to it. The most effective defense against this dangerous illness is vaccination.
What is Meningitis B?
Meningitis B refers to meningitis caused by Neisseria meningitidis serogroup B bacteria. This type of bacterial meningitis is severe and can lead to death or serious long-term consequences like brain damage, hearing loss, and learning disabilities.
Who Should Get the Meningitis B Vaccine?

The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends the meningococcal B vaccine for:
Adolescents and young adults aged 16–23 years, preferably at 16–18 years.
People aged 10 years or older who are at increased risk for serogroup B meningococcal infections, such as those with certain medical conditions or who are taking certain medications.
Those who are at increased risk because of an outbreak of serogroup B meningococcal disease.
Vaccine Schedule and Side Effects
here are two types of meningitis B vaccines available in the United States: Bexsero and Trumenba. The vaccination schedule varies slightly between these two:
- Bexsero: Two doses administered at least one month apart.
- Trumenba: Three doses, with the second dose given two months after the first and the third dose given six months after the first.
Common side effects include:
- Soreness at the injection site
- Fatigue
- Headache
- Muscle or joint pain
- Fever
Importance of Vaccination
Meningococcal infections can cause serious health problems or even death in a matter of hours, even with treatment, which is why vaccination is so important. Adolescent and young adult vaccinations can dramatically lower the likelihood of epidemics in places like college campuses.
Meningitis NCLEX Questions
For nursing students preparing for the NCLEX-RN exam, understanding meningitis is essential. Here are some common types of NCLEX questions related to meningitis, focusing on symptoms, nursing interventions, and patient education.
Symptom Identification
Question 1: A 20-year-old college student comes to the clinic complaining of a severe headache, fever, and stiff neck. Which of the following should the nurse suspect?
- A) Influenza
- B) Migraine
- C) Meningitis
- D) Tension headache
Answer: C) Meningitis
Nursing Interventions
Question 2: The nurse is caring for a patient with suspected bacterial meningitis. What is the priority nursing intervention?
- A) Administer antipyretics as ordered.
- B) Monitor the patient’s neurological status every 4 hours.
- C) Initiate isolation precautions.
- D) Provide a quiet, dark environment to reduce stimulation.
Answer: C) Initiate isolation precautions.
Patient Education
Question 3: What should the nurse include in the discharge teaching for a patient recovering from bacterial meningitis?
- A) Avoid all physical activities for the next six months.
- B) Follow up with hearing tests as auditory damage is a common complication.
- C) There is no need for further vaccinations after recovery.
- D) Dietary restrictions are necessary for the next month.
Answer: B) Follow up with hearing tests as auditory damage is a common complication.
Medication Administration
Question 4: A patient with bacterial meningitis is prescribed intravenous antibiotics. The nurse understands that the rationale for this treatment is:
- A) To reduce inflammation.
- B) To prevent the spread of infection to others.
- C) To eliminate the bacterial infection in the central nervous system.
- D) To alleviate pain and discomfort.
Answer: C) To eliminate the bacterial infection in the central nervous system.
NCLEX Meningitis Questions
Here are additional NCLEX-style questions focusing on different aspects of meningitis care.
Diagnostic Procedures
Question 1: Which diagnostic test is most definitive for diagnosing meningitis?
- A) Complete blood count (CBC)
- B) Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- C) Lumbar puncture with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis
- D) Computed tomography (CT) scan
Answer: C) Lumbar puncture with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis
Risk Factors
Question 2: Which of the following patients is at highest risk for developing bacterial meningitis?
- A) A 3-month-old infant
- B) A 25-year-old healthy adult
- C) A 16-year-old adolescent
- D) A 70-year-old adult with a history of hypertension
Answer: A) A 3-month-old infant
Infection Control
Question 3: The nurse is providing care to a patient with meningococcal meningitis. Which infection control precautions should be implemented?
- A) Standard precautions
- B) Contact precautions
- C) Droplet precautions
- D) Airborne precautions
Answer: C) Droplet precautions
Complications
Question 4: A patient with meningitis is being monitored for potential complications. Which of the following findings should the nurse report immediately?
- A) Elevated blood pressure
- B) Decreased urine output
- C) Bradycardia
- D) Seizures
Answer: D) Seizures
Follow-Up Care
Question 5: What follow-up care is important for a patient who has been treated for bacterial meningitis?
- A) Regular blood pressure monitoring
- B) Routine liver function tests
- C) Audiology exams to check for hearing loss
- D) Annual flu vaccinations
Answer: C) Audiology exams to check for hearing loss
By understanding these questions and their rationale, nursing students can better prepare for the NCLEX and provide high-quality care to patients with meningitis.
In conclusion, being aware of the symptoms of meningitis, the importance of vaccination, and the necessary nursing interventions can significantly impact patient outcomes. Whether you are a student preparing for exams or someone looking to understand this condition better, this guide provides essential information to help you navigate the complexities of meningitis.