Overview
One of the most prevalent types of infections in your urinary system is a urinary tract infection. Any component of your urinary system may be affected. Most frequently, bacteria—particularly E. coli—cause urinary tract infections. Frequent urination, pain during urination, and soreness in the side or lower back are among the symptoms. Most UTIs can be treated with antibiotics.
What is a urinary tract infection (UTI)?
An infection of the urinary system is known as a urinary tract infection (UTI). This kind of illness may affect one of your:
Urinarytract (urethritis).
kidneys (arthritis pyelinose).
bladder (cystitis).
A result of your kidneys’ blood-filtering function is urine, or pee. When your kidneys filter out waste materials and extra water from your blood, pee is produced. Normally, urine passes through your urinary tract cleanly. On the other hand, bacteria can enter your urinary system and lead to UTIs.
What is the urinary tract?
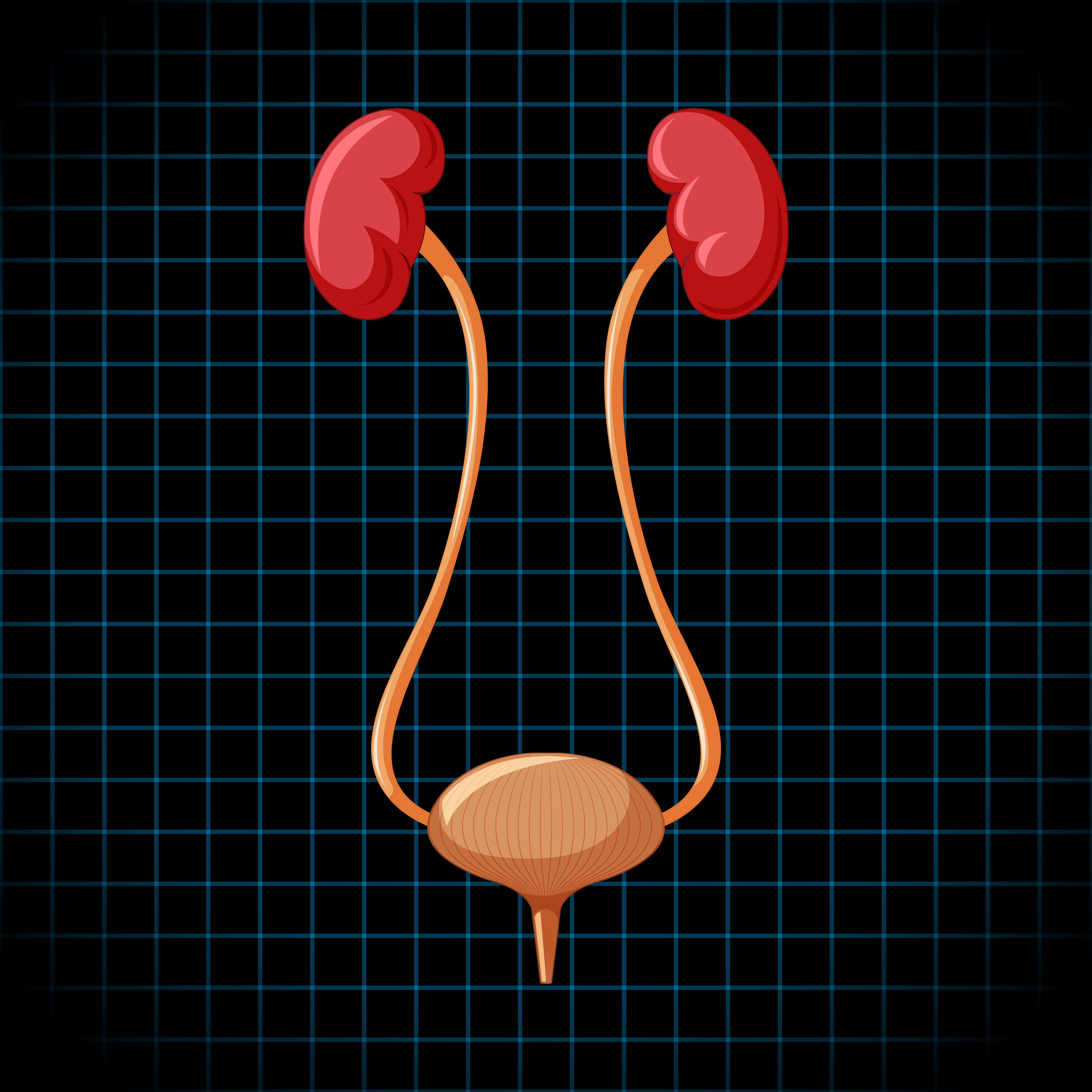
The urinary system produces and stores urine. Among them are your:
Kidneys.The kidneys are small, bean-shaped organs located above the hips on the back of the body. The average person has two kidneys. Your blood is filtered to remove waste materials and water, resulting in urine. Two common wastes are creatinine and urea.
Ureters. Urine is transported from your kidneys to your bladder through tiny tubes called ureters.
bladder. Before it leaves your body, urine is stored in your bladder, an organ that resembles a balloon.
Urethra. Urine is transported from your bladder to the exterior of your body through the urethra.
How common are urinary tract infections?
UTIs are extremely frequent, particularly in female-assigned birth cohorts (AFAB) and women. UTIs affect almost half of AFAB individuals at some time in their lives. Though they only affect 1% to 2% of infants, UTIs can also affect men and persons designated male at birth (AMAB). So can children. Eight million to ten million UTIs are treated annually by healthcare professionals.
Symptoms and Causes

What are the signs of a urinary tract infection?
Urinary tract lining inflammation is brought on by a UTI. The following issues could be brought on by the inflammation:
You may be experiencing lower back, pelvic, flank, or abdomen pain.
pressure in your pelvis’ lower region.
murky, bad-smelling poop.
incontinence in the urine.
a lot of urine production.
Encourage incontinence.
pain while urination (dysuria).
Urine with blood in it (hematuria).
Other UTI-associated symptoms may include:
- Pain in your penis.
- Feeling extremely tired (fatigue).
- Fever.
- Chills.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Mental changes or confusion.
How do you get a urinary tract infection?
Urinary tract infections are caused by microorganisms, primarily bacteria. They may infect your bladder and usually enter through your urethra. Additionally, the infection may ascend from your bladder via your ureters and ultimately affect your kidneys.
What is the major cause of a urinary tract infection?
![]()
E. coli cause more than 90% of bladder infections. E. coli typically exist in your lower intestines (large intestine).
Who is at the greatest risk of getting a urinary tract infection?
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) can affect anyone, although vaginal infections are more common in those who have them. This is because persons with AFAB have shorter urethras that are located closer to the anus, which is a typical site for E. Coli bacteria.
Can you get a UTI from fingers?
It is true that a UTI can originate from the fingertips. Every time you contact a surface, bacteria and other microorganisms might enter your hands. When you use the restroom or engage in sexual activities like fingering or masturbating, you may unintentionally introduce bacteria into your urethra.
Hand washing is an excellent practice both before and after using the restroom or having sex.
Diagnosis and Tests

How do you know if you have a UTI?
If you have symptoms of a urinary tract infection, talk to a healthcare provider. They’ll ask questions about your symptoms, review your medical history and conduct a physical examination. They can also order tests to help confirm a diagnosis.
What tests will be done to diagnose a urinary tract infection?
To identify a UTI, a medical professional may request the following tests:
Urinalysis. You are going to urinate into a specific cup during this test. The sample will be sent by the provider to a lab, where trained personnel will use various tests, including nitrites, leukocyte esterase, and white blood cells, to check for indications of a urinary tract infection.
urine culture. You will pee into a designated cup, and lab personnel will examine your specimen to detect the presence of any bacteria. Urine cultures are crucial since they assist your doctor in deciding on the best course of action.
A healthcare professional may prescribe the following tests to check your urinary tract for an illness or injury if your infection doesn’t go away after treatment:
ultrasonic. An ultrasound is a diagnostic procedure that allows your physician to view your interior organs. There is no need for preparation and an ultrasonography is painless.
CT scan, or computed tomography. An additional imaging test is a CT scan. This kind of X-ray creates three-dimensional images of your insides by taking cross-sectional pictures of your body, or slices. An X-ray is not as accurate as a CT scan.
Cystoscopy. During a cystoscopy, a cystoscope is used to examine through your urethra into your bladder. A narrow device with a lens and a light at the end is called a cystoscope.
Management and Treatment
What is the best thing to do for a urinary tract infection?
The best course of action for a urinary tract infection is to visit a doctor. To treat a UTI, you must take antibiotics. An antibiotic that is most effective against the germs causing your infection will be chosen by your healthcare professional.
It’s crucial that you abide by the prescription’s instructions after you receive one for antibiotics. Even if you start feeling better and your symptoms go away, make sure you finish the entire course of antibiotics. If you don’t take the entire prescribed amount, the infection may return and become harder to cure.
What specific antibiotics are used to treat a urinary tract infection?
Healthcare providers commonly prescribe the following antibiotics to treat UTIs:
- Nitrofurantoin.
- Sulfonamides (sulfa drugs), such as sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim.
- Amoxicillin.
- Cephalosporins, such as cephalexin.
- Doxycycline.
- Fosfomycin.
- Quinolones, such as ciprofloxacin or levofloxacin.
If you frequently experience urinary tract infections, your doctor might prescribe low-dose antibiotics for a brief period of time to stop the illness from returning. Your doctor might advise you to use this cautious approach when treating recurrent UTIs since you run the risk of developing antibiotic resistance and contracting additional illnesses, such as C. diff colitis. This is not a particularly widespread practice.
Can I become immune to the antibiotics used to treat a UTI?
Kind of. Antibiotic resistance is the result of the infection becoming more resistant to antibiotics each time they are used to treat a UTI. However, the infection—not you—becomes resistant to the antibiotics. Using antibiotics isn’t always the best course of action. Because of this, if you have recurrent UTIs, your doctor might recommend different courses of action.
Does cranberry juice prevent a urinary tract infection?
The grocery store brand of cranberry juice does not shield you from getting a UTI. On the other hand, cranberry extract supplements, or vitamin tablets, might lower your risk of UTIs.
Prevention
Can I prevent a urinary tract infection?
Urinary tract infections can be avoided by adopting the following lifestyle modifications:
Maintain proper hygiene.
One of the most effective strategies to help avoid UTIs is to practice excellent cleanliness. This is particularly critical if you vaginally absorb birth since, due to the shorter urethra, E. Coli finds it easy to return from your rectum into your body. To prevent this, always wipe after a bowel movement (pooping) from front to back.
Drink plenty of fluids
Drinking extra fluids — especially water — each day can help flush out bacteria from your urinary tract. Healthcare providers recommend drinking six to eight glasses of water daily.
Change your peeing habits
Peeing can play a big role in getting rid of bacteria from your body. Your pee is a waste product, and each time you empty your bladder, you help remove that waste from your body.
Additional Common Questions
What are symptoms of UTI in females?
They may result in: the need to urinate more frequently than usual.
discomfort or agony during urinating.
sudden urinal cravings.
having the sensation that you can’t completely empty your bladder.
discomfort in the lower abdomen.
urine with a murky, unpleasant smell, or blood in it.
feeling overall ill, sore, and exhausted.
What is the cause of a urinary tract infection?
The most common cause of urinary tract infections (UTIs) is bacteria from feces getting into the urinary system. The urethra, the tube that exits the body with urine, is where the germs enter. Compared to men, women’s urethras are shorter. This indicates that there is a higher chance of bacteria entering the bladder or kidneys and infecting them.
How to clean your bladder naturally?
To improve the health of your bladder,
try these simple steps.
Sip some water.
Maintaining hydration is essential.
Add the lime and the lemon.
Select unsaturated fats.
Use extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) on a daily basis.
Vegetables and fruits are essential.
Include cruciferous veggies in your diet.
Steer clear of bladder irritants