Overview
One of the most prevalent types of infections in your urinary system is a urinary tract infection. Any component of your urinary system may be affected. Most frequently, bacteria—particularly E. coli—cause urinary tract infections. Frequent urination, pain during urination, and soreness in the side or lower back are among the symptoms. Most UTIs can be treated with antibiotics.
What is a urinary tract infection (UTI)?
An infection of the urinary system is known as a urinary tract infection (UTI). This kind of illness may affect one of your:
Urethra
Kidneys
Bladder
A result of your kidneys’ blood-filtering function is urine, or pee. When your kidneys filter out waste materials and extra water from your blood, pee is produced. Normally, urine passes through your urinary tract cleanly. On the other hand, bacteria can enter your urinary system and lead to UTIs.
What is the urinary tract?
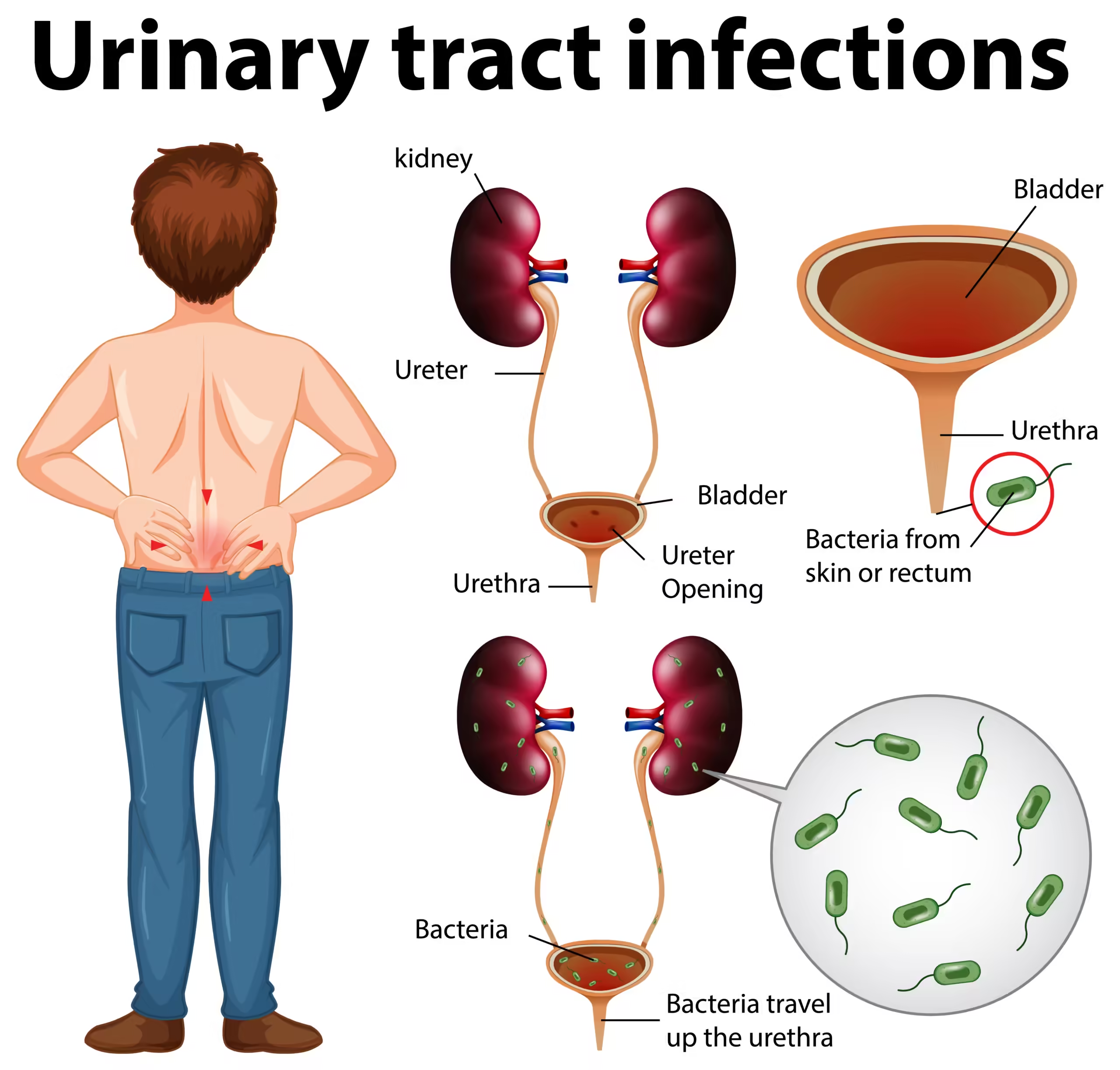
![]()

The urinary system produces and stores urine. Among them are your:
kidneys. The kidneys are small, bean-shaped organs located above the hips on the back of the body. The average person has two kidneys. Your blood is filtered to remove waste materials and water, resulting in urine. Two common wastes are creatinine and urea.
Ureters. Urine is transported from your kidneys to your bladder through tiny tubes called ureters.
bladder. Before it leaves your body, urine is stored in your bladder, an organ that resembles a balloon.
Urethra. Urine is transported from your bladder to the exterior of your body through the urethra.
How common are urinary tract infections?
UTIs are extremely frequent, particularly in female-assigned birth cohorts (AFAB) and women. UTIs affect almost half of AFAB individuals at some time in their lives. Though they only affect 1% to 2% of infants, UTIs can also affect men and persons designated male at birth (AMAB). So can children. Eight million to ten million UTIs are treated annually by healthcare professionals.
Symptoms and Causes
What are the signs of a urinary tract infection?
A UTI causes inflammation in the lining of your urinary tract. The inflammation may cause the following problems:
Pain in your flank, stomach, pelvic place or lower lower back.
Pressure inside the decrease part of your pelvis.
Cloudy, foul-smelling pee.
Urinary incontinence.
Frequent urination.
Urge incontinence.
Pain when you pee (dysuria).
Blood on your pee (hematuria).
Other UTI-associated symptoms may include.
You feel pain in your penis.
having a severe case of tiredness.
High temperature.
Feels cold.
vomiting as well as nausea.
Disorientation or mental alterations.
How do you get a urinary tract infection?
Urinary tract infections are caused by microorganisms, primarily bacteria. They may infect your bladder and usually enter through your urethra. Additionally, the infection may ascend from your bladder via your ureters and ultimately affect your kidneys.
What is the major cause of a urinary tract infection?
More than 90% of bladder infections are caused by E. coli. Usually, E. Coli is found in your lower intestines.
Who is at the greatest risk of getting a urinary tract infection?
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) can affect anyone, although vaginal infections are more common in those who have them. The urethra of AFAB individuals is shorter and situated toward the anus, an area where E. Coli germs are frequently found.
Diagnosis and Tests
How do you know if you have a UTI?
![]()
Speak with a healthcare professional if you experience any urinary tract infection-related symptoms. Along with reviewing your medical history and performing a physical examination, they will enquire about your symptoms. In order to aid confirm a diagnosis, they can also prescribe testing.
What tests will be done to diagnose a urinary tract infection?
A healthcare issuer can also order the subsequent exams to diagnose a UTI:
Urinalysis. During this take a look at, you’ll pee into a special cup. The provider will ship the sample to a laboratory, in which technicians will look at it for signs of a UTI the use of multiple variables including nitrites, leukocyte esterase and white blood cells.
Urine lifestyle. You’ll pee right into a special cup, and lab technicians will check your pattern to develop and identify any bacteria which can be gift. Urine cultures are critical because they assist your issuer determine the most appropriate remedy
Management and Treatment
What is the best thing to do for a urinary tract infection?
The exceptional thing to do for a urinary tract contamination is to look a healthcare provider. You want antibiotics to treat a UTI. Your provider will pick an antibiotic that works first-rate against the micro organism answerable for your contamination.
Once you get a prescription for antibiotics, it’s very crucial which you comply with the instructions for taking them. Be certain to take the total path of antibiotics, even if your signs and symptoms leave and also you begin feeling better. If you don’t finish all of your medicine, the infection can go back and be more hard to treat.
Prevention
Can I prevent a urinary tract infection?
The following lifestyle changes can help prevent urinary tract infections:
Practice good hygiene
One of the most effective strategies to help avoid UTIs is to practice excellent cleanliness. This is particularly critical if you vaginally absorb birth since, due to the shorter urethra, E. Coli finds it easy to return from your rectum into your body. To prevent this, always wipe after a bowel movement (pooping) from front to back.
It is also a good idea to replace your period goods, such as pads and tampons, on a regular basis during your menstrual cycle. Moreover, you ought to refrain from applying deodorant on your vagina.
Drink plenty of fluids
Increasing your daily fluid intake, particularly with water, can aid in the removal of bacteria from your urinary system. Medical professionals advise consuming six to eight glasses of water each day.
Change your peeing habits
One of the main ways to remove bacteria from your body is to urinate. Every time you let go of your bladder, you are aiding in the removal of waste from your body, which is your urine.
Especially if you frequently get UTIs, urinating frequently can lower your risk of contracting an infection.
Moreover, you ought to make an effort to urinate both before and after having sex. Urinating before and after sex helps remove bacteria that may be introduced to your urethra during sexual activity. Wash the region with warm water if you are unable to urinate.
What can I expect if I have a urinary tract infection?
Urinary tract infections have an excellent prognosis. Treatment for most UTIs usually has a very positive effect. Prior to beginning therapy, a UTI may cause irritation or discomfort. However, your symptoms ought to get better right away if a medical professional finds the germs and gives you the right treatment.
It’s critical that you take all antibiotics as prescribed by your doctor. Your doctor may run tests to see whether your infection is resistant to antibiotics if you get UTIs frequently or if your symptoms don’t get better. IV antibiotics or other treatments may be necessary for illnesses resistant to antibiotics.
What is the difference between a urinary tract infection and cystitis?
An infection of the urinary tract, which includes the bladder, ureters, kidneys, and urethra, is known as a UTI. An example of a UTI is cystitis. It is the most prevalent type of UTI and is an infection in your bladder.