What Is Colorectal Cancer?
Colorectal most cancers is a disorder wherein cells inside the colon or rectum develop out of manage. Sometimes it’s miles called colon cancer, for short. The colon is the large intestine or huge bowel. The rectum is the passageway that connects the colon to the anus.
Sometimes odd growths, referred to as polyps, form within the colon or rectum. Over time, a few polyps may change into cancer. Screening tests can find polyps so that they can be removed earlier than turning into cancer. Screening additionally allows locate colorectal cancer at an early level, while treatment works excellent.
What Are the Symptoms of Colorectal Cancer?
Colorectal polyps (bizarre growths in the colon or rectum that may develop into cancer if not removed) and colorectal most cancers don’t continually purpose signs, especially at first. Someone should have polyps or colorectal most cancers and now not realize it. That is why getting screened often for colorectal cancer is so essential.
If you have signs, they will consist of:
A trade in bowel conduct.
Blood in or in your stool (bowel movement).
Diarrhea, constipation, or feeling that the bowel does not empty all the way.
Abdominal pain, aches, or cramps that don’t depart.
Weight loss and you don’t know why.
Colon cancer complications
Colon cancer headaches can be critical. They include perforation of the colon, obstruction, and bleeding.
When untreated, colorectal cancer can reason bowel obstruction, can unfold cancer to other tissues or organs (metastasis), and may grow to be 2d number one colorectal most cancers.
Colon Cancer Diagnosis
Diagnosis of colorectal most cancers regularly begins with a screening to evaluate whether signs point to cancer. If a gastroenterologist suspects colorectal most cancers, a biopsy is suggested and then accomplished throughout a colonoscopy. During the colonoscopy, a medical doctor will dispose of a small sample of tissue with a device that is surpassed via the scope. In much less commonplace instances, part of the colon might want to be surgically eliminated to make a analysis.
Samples are then dispatched to the lab for exam. If most cancers is discovered, different checks might be achieved to greater appropriately classify the cancer and decide treatment options. Those tests may encompass biomarker checking out, that is routine in assessing colorectal most cancers. This type of trying out provides oncologists with extra statistics about the kind of cancer they are treating by using examining genes, proteins, or other pieces of biological records, all of which might be referred to as biomarkers.
These biomarkers offer clues as to how most cancers develops. With this data, oncologists can take a more targeted technique to treating each case of colorectal cancer. More targeted remedies can cause higher remedy results for human beings with colorectal cancer.
For example, a health practitioner will in all likelihood order biomarker tests—which include for mutations of the genes KRAS, NRAS, and BRAF—to decide which capsules may be considered for treatment. A physician may additionally order microsatellite instability (MSI) and mismatch repair (MMR) checking out to check for a probable connection with Lynch syndrome.
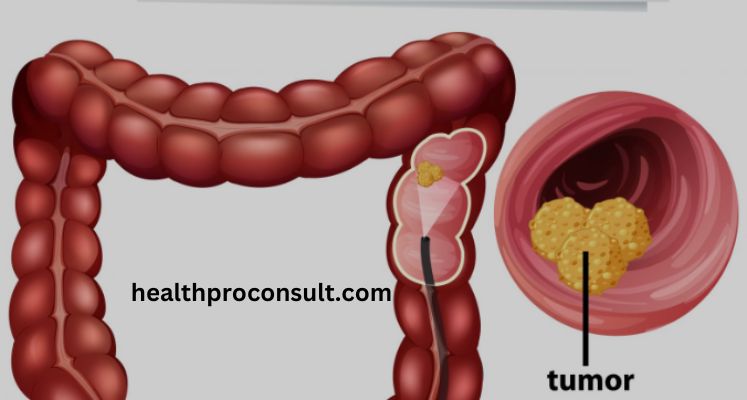
How does colorectal cancer start?
Polyps inside the colon or rectum
Most colorectal cancers begin as a growth on the inner lining of the colon or rectum. These growths are called polyps.
Polyps are quite not unusual, specifically as you get older. Most polyps are benign, or noncancerous. Some sorts of polyps can alternate into most cancers over the years (commonly over many years). The hazard of a polyp turning into cancer depends on the sort of polyp it’s miles. There are different varieties of polyps.
Adenomatous polyps (adenomas): These polyps sometimes alternate into cancer. Because of this, adenomas are called a precancerous condition. The three sorts of adenomas are tubular, villous, and tubulovillous. Tubular adenomas are the maximum commonplace sort of adenomatous polyps. Villous adenomas are the least common kind of adenomatous polyps, however are more likely to change into cancer.
Hyperplastic polyps and inflammatory polyps: These polyps are greater common, however in general they may be not precancerous. Some people with big (extra than 1cm) hyperplastic polyps may want colorectal cancer screening with colonoscopy extra regularly.
Sessile serrated polyps (SSP) and conventional serrated adenomas (TSA): These polyps are frequently treated like adenomas due to the fact they have got a better threat of changing into cancer.
Other factors which can make a polyp more likely to contain most cancers or increase someone’s hazard of developing colorectal cancer include:
Size: If a polyp large than 1 cm
Number: If greater than three polyps are found
Histology: If dysplasia is seen in the polyp. Dysplasia approach that the cells appearance extraordinary, but they haven’t yet come to be most cancers.
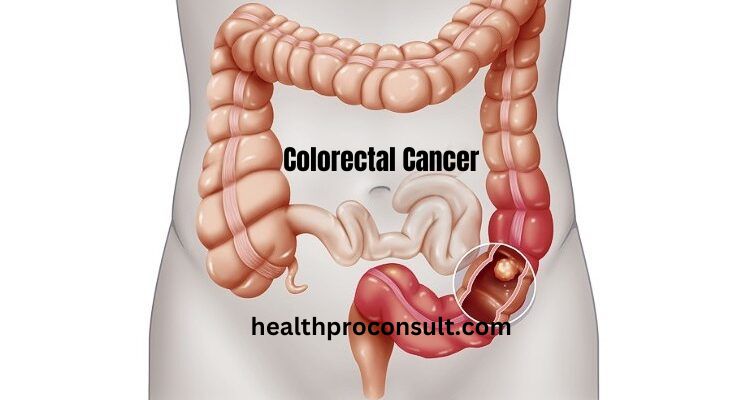
How colorectal cancer spreads?
If most cancers form in a polyp, it could grow into the wall of the colon or rectum through the years. The wall of the colon and rectum is made of many layers. Colorectal most cancers begins in the innermost layer (the mucosa) and might develop outward thru a few or all of the other layers (see picture underneath).
When cancer cells are within the wall, they could then grow into blood vessels or lymph vessels (tiny channels that bring away waste and fluid). From there, they can journey to nearby lymph nodes or to remote elements of the body.
The stage (quantity of unfold) of a colorectal most cancers relies upon on how deeply it grows into the wall and if it has unfolded outside the colon or rectum.
Types of cancer in the colon and rectum
Most colorectal cancers are adenocarcinomas. These cancers start in cells that make mucus to lubricate the inner of the colon and rectum. When docs talk about colorectal most cancers, they’re nearly continually talking approximately this kind. Some subtypes of adenocarcinoma, inclusive of signet ring and mucinous, might also have a worse analysis (outlook) than other subtypes of adenocarcinoma.
Carcinoid tumors. These start from unique hormone-making cells within the gut.
Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) begin from nerve cells inside the wall of the gastrointestinal tract. Some are benign (no longer most cancers). These tumors are maximum generally determined inside the stomach and small intestine. They are not usually determined within the colon or rectum
Lymphomas are cancers of immune machine cells. They broadly speaking start in lymph nodes, but they can also begin in the colon, rectum, or other organs. Information on lymphomas of the digestive system may be located in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma.
Sarcomas can start in blood vessels, muscle layers, or different connective tissues within the wall of the colon and rectum. Sarcomas of the colon or rectum are uncommon






2 thoughts on “Colorectal Cancer”